HOWTO: Enable Docker API through firewalld on CentOS 7.x (el7)
 Playing more and more with Docker across multiple Linux distributions has taught me that not all Linux distributions are treated the same.
Playing more and more with Docker across multiple Linux distributions has taught me that not all Linux distributions are treated the same.
There’s a discord right now in the Linux community about systemd vs. SysV init. In our example, CentOS 7.x uses systemd, where all system services are spawned and started.
I am using this version of Linux to set up my own Docker lab host for tire-kicking, but it needs some tweaks.
I also wanted to see if I could use the Docker API from my Android phone, using DockerDroid, which (after configuring this) works famously!
Here’s what you need to do:
- Log into your CentOS machine and update to the most-current Docker version. The version shipped with CentOS 7 in the repo as I write this post, is “docker-1.3.2-4.el7.centos.x86_64”. You want to be using something more current, and 1.4 is the latest. To fetch that (and preserve your existing version), run the following:
$ su - # cd /bin && mv /bin/docker /bin/docker.el7 # wget https://get.docker.com/builds/Linux/x86_64/docker-latest -O docker # systemctl restart docker # exit $
Now you should have a working Docker with the right version (current). You can verify that:
$ sudo docker version Client version: 1.4.1 Client API version: 1.16 Go version (client): go1.3.3 Git commit (client): 5bc2ff8 OS/Arch (client): linux/amd64 Server version: 1.4.1 Server API version: 1.16 Go version (server): go1.3.3 Git commit (server): 5bc2ff8
- So far, so good! Now we need to make sure firewalld has a rule to permit this port to be exposed for external connections:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4243/tcp --permanent $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload success
You can verify that this new rule was added, by looking at /etc/firewalld/zones/public.xml, which should now have a line that looks like this:
<port protocol="tcp" port="4243"/>
- Now let’s reconfigure Docker to expose the API to external client connections, by making sure the OPTIONS line in /etc/sysconfig/docker looks like this (note the portion in bold):
OPTIONS=--selinux-enabled -H fd:// -H tcp://0.0.0.0:4243
- Restart the Docker service to enact the API on that port (if successful, you will not see any output):
sudo systemctl restart docker
- To test the port locally, install telnet and then try telnet’ing to the port on localhost:
$ sudo telnet localhost 4243 Trying ::1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request Connection closed by foreign host.
All looks good so far!
- Lastly, install DockerDroid and configure it to talk to your server on this port:
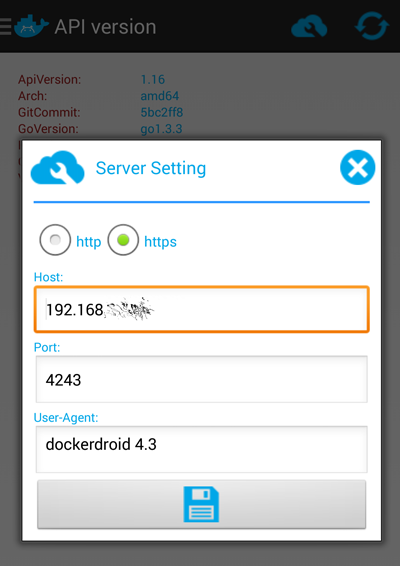
Now you should be able to use DockerDroid to navigate your Images, Containers and API.
Good luck!
