Archive for the 'Security' Category
HOWTO: Run multiple copies of Signal Messenger on your desktop/laptop
Tags: Privacy, security, SignalThis question has been asked many dozens of times for the last several years, and to-date, has not been solved in the core project itself. There were many attempts, hacks and workarounds, but nothing really supportable.
Let’s say you have two devices, a Personal phone and a Work phone, each running Signal. You want to be able to load one app and have conversations that span both devices. That is, converse with work colleagues and also converse with personal colleagues, from one desktop.
Today, you can’t. Well, not without some additional setup to do so.
To make this work, you’ll need to create a separate data directory for each “profile” you intend to use, and then configure Signal to refer to it when launching them. You can then tie these to a launcher or icon if you wish, in your favorite OS of choice (Linux and macOS are mine, macOS and Windows for others).
Your normal Signal data resides in a directory under your $HOME named ~/.config/Signal by default. Let’s make another to use for testing with your second device. Intuitively, you can name them by the device they are used with, so ~/.config/Signal-iPhone and ~/.config/Signal-Android for example on a POSIX based OS like Linux or macOS. On Windows, this will be stored in C:\Users\You\AppData\Roaming\Signal.
If you’re already using Signal on your desktop, your profile data will just be in the ~/.config/Signal directory, and you don’t need to change it. In fact, renaming it will likely break things until we create these additional profiles. Create a second directory at the same level as the existing one, for use with that second profile.
Now we need to launch Signal from the shell (Terminal in macOS, Command Prompt in Windows), and run it as follows:
/Applications/Signal.app/Contents/MacOS/Signal --user-data-dir=$HOME/.config/Signal-iPhone
This should prompt you to scan a QR code with your phone, to link the two devices, similar to the following:
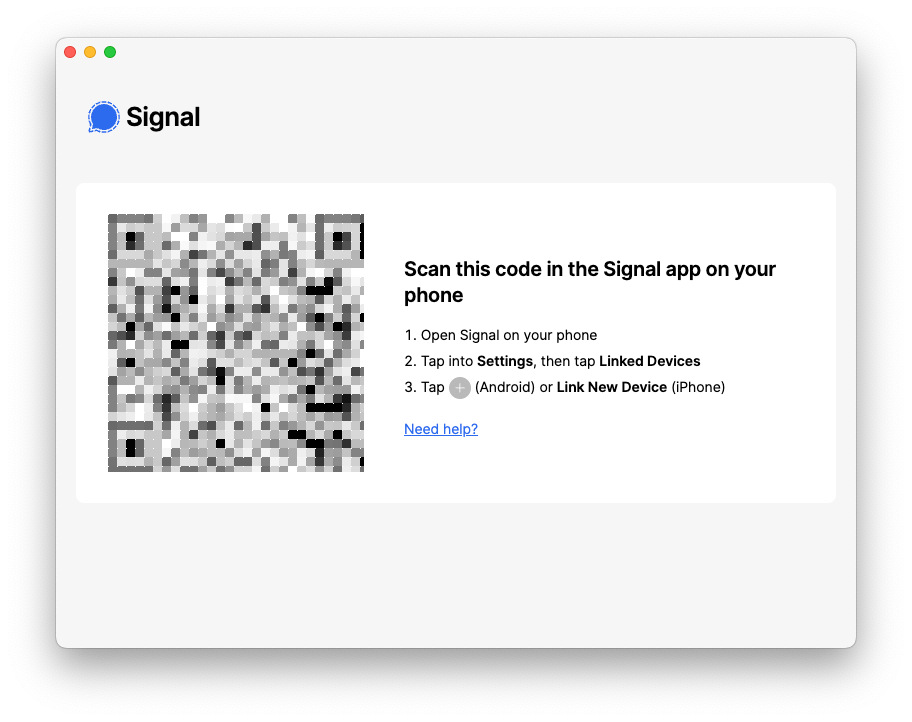
On your mobile device, go to Settings ? Linked Devices, and scan that QR code. It will now pair your phone with this instance of Signal Desktop.
So far, so good. Now while that is synchronizing your data, launch the other instance of Signal with the standard launcher. You should now get two instances of Signal Desktop running, one linked with your original mobile device, and this new instance linked with your second mobile device.
Ta-da! You did it.
Now let’s codify these changes into their own respective launchers/icons, so you don’t have to use the shell/Terminal/Command Prompt to do this each time.
On Linux, just create a launcher using your window manager that sets those commandline args as the default.
On macOS, you can create a new launcher for Signal with Automator, by choosing “Run Shell Script” from the Workflow menu. Double-click that, and a window will open to the right, allowing you to type in your shell commands. Mine is as follows, just like we ran from Terminal:
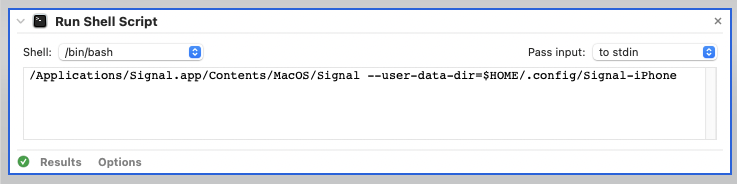
Click “Run” in the upper-right, to ensure it does indeed run Signal Desktop with your second (new) profile correctly. If it does, you can save it as a “Workflow” or an “Application”. I chose the latter, which looks like this:
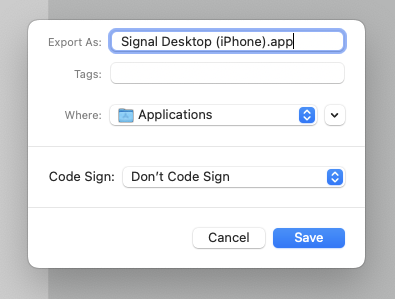
Now you have your intended commands tied to an application launcher, which can be put into your Dock or other launcher location.
On Windows, you’ll need to create a new desktop shortcut by going to Preferences, and change the target to: C:\Users\You\AppData\Local\Programs\signal-desktop\Signal.exe --user-data-dir=C:\Users\You\AppData\Roaming\Signal-iPhone. You can choose any icon you wish to adorn this shortcut with.
That’s it! You now have a multi-Signal Desktop solution (that is, until the upstream project adds profile support to a newer release).
Have fun, and keep those messages secure!
HOWTO: Fully automated Zwift login on Mac OS X
 Quite a few riders on the Facebook Zwift Riders group have expressed an interest in this, so I decided to take a couple of hours, learn AppleScript and knock this out. Done! (if you’re on Windows, you want this other HOWTO instead)
Quite a few riders on the Facebook Zwift Riders group have expressed an interest in this, so I decided to take a couple of hours, learn AppleScript and knock this out. Done! (if you’re on Windows, you want this other HOWTO instead)
What this code does, is allows you to create a single icon that will log you into Zwift, with no human interaction needed. It will put in your email, password, click the “Start Ride” button and away you go!
This also leverages the OS X Keychain to store your Zwift email address and password, so it’s secure, not leaked into the filesystem and is able to be called on by any other apps that might need it (ahem, like… Zwift itself!) :D
So here’s how to get it working…
First, we need to create a separate keychain to store the Zwift credentials. You could store them in the main keychain, but I’m a fan of credential separation, so let’s use that.
Read the rest of this entry »
HOWTO: Remove the “Year in Review” Posts from your Facebook Wall
It’s annoying. It’s Facebook. We all learn to either love or hate it, but there are ways to make the annoying parts of it go away.
The most-recent annoyance is Facebook’s compulsion to add the “Year in Review” posts from people to your Facebook wall.
Thankfully I’ve never been asked to fill mine out, but I do see hundreds of these from other “Friends” of mine. It looks like this:
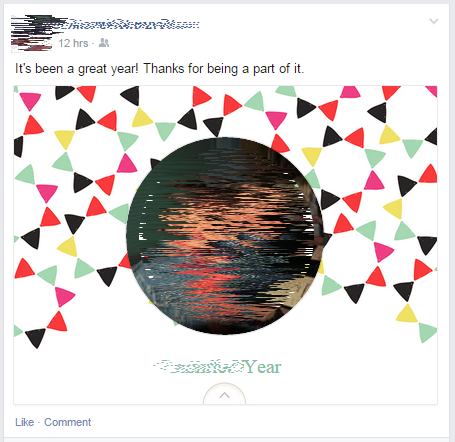
Here’s how to get rid of them:
-
Log into Facebook and go to this page:
-
Once you get there, you’ll see a section near the bottom labeled “Block Pages”. Put “YearInReview” into that form and hit Enter.
-
If you’ve done it right, you should see something like this:
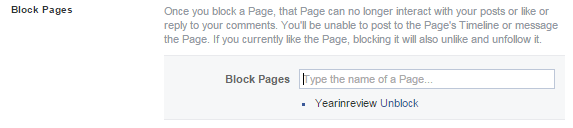
That’s it, you’re done!
If you want to get rid of more Facebook garbage, ads and other annoyances, you can install the “Social Fixer” browser extension in your browser of choice. There are versions for Safari, Chrome, Firefox and Microsoft Internet Explorer. Works great!
SOLVED: Fixing Perl Plug-ins for XChat Azure in OS X Mavericks 10.9
I’m a heavy user of IRC and have been since the late 90’s. I use X-Chat for IRC on almost all machines, including Mac and Windows, not just the Linux environment that it was created upon.
When I recently upgraded my OS X Lion (10.7.5) machine to OS X Mavericks (10.9), I started seeing a significant amount of core OS bugs. One of them affected how I use XChat to get to Freenode and other networks via SASL, SSL and Tor.
If you’re using XChat Azure 1.16.0 or the latest preview of 1.16.1, you’ll see the following errors when trying to load Perl plugins from Window -> Plugins and Scripts inside XChat:
Invalid Mac OS X bundle or required Mac OS X version is not satisfied
You’ll see this when you try to select the version of Perl showing in the Plugins window. The Python plugin works fine, just not Perl.
Here’s the quick-and-dirty fix, until the XChat Azure team can come out with a Mavericks-compatible release that uses the latest Perl:
Change to the XChat Azure PlugIns directory:
cd /Applications/XChat Azure.app/Contents/PlugIns/
Duplicate the contents of the perl-lion Perl bundle into one for Mavericks
sudo rsync -avP perl-lion.bundle/. perl-mavericks.bundle
Update the Info.plist file to match the versioning:
sudo defaults write ./perl-mavericks.bundle/Contents/Info XChatAquaMacOSVersionBranch 10.9
There’s one last step I found when I ran that last command to update Info.plist, and that is that you have to hand-modify the version in the .plist file to match OS X Mavericks 10.9 versioning:
sudo vi perl-mavericks.bundle/Contents/Info.plist
Down near the bottom of the file, change the string value of XChatAquaMacOSVersionBranch from 10.6 to 10.9, like this:
<key>XChatAquaMacOSVersionBranch</key>
<string>10.9</string>
Now if you go quit and restart XChat Azure, go to Window -> Plugins and select your Perl interpreter (the one with 10.9), it will work, and you’ll see your plugins loaded as expected:
[16:27] Python interface loaded [16:27] Perl interface loaded [16:27] SASL: auth loaded from /Users/$USER/Library/Containers/org.3rddev.xchatazure/Data/Library/Application Support/XChat Azure/sasl.auth
I wrote some HOWTO documents describing how to configure Tor + SASL + SSL to connect to IRC, you can find them here:
- HOWTO: Configure Tor + SASL + irc to connect to Freenode
- HOWTO: Configure XChat Azure on OS X to connect to Freenode using SASL + Tor
That’s it! Good luck and happy IRC’ing!
How Many Java Versions is Enough for Mavericks, Apple?
 A lot of software outright fails to work on Apple OS X Mavericks.
A lot of software outright fails to work on Apple OS X Mavericks.
It’s a disaster. Almost nothing works right.
Not only is the entire OS noticeably slower, by several orders of magnitude over the previous Lion (10.7.5) was running until a few days ago on my 11″ MacBook Air, but there are dozens and dozens of glaringly-obvious bugs that make me want to go back to my Linux laptop full-time.
Here are some obvious ones:
- The trackpad randomly disables two-finger scrolling and the only way to get it back is to either log out and back in, or restart the machine entirely.
- The direction of the trackpad scrolling was reversed after the upgrade. Dragging fingers down, used to pull the page down, now it pulls the page up. You can flip the toggle to reverse it, but why was it changed at all from the default?
- The audio up/down buttons are about 1-2 seconds behind the actual button press, which is a bit disjointed when you’re trying to determine how far down or up to change the volume for a video or song.
- USB Ethernet used to work plug-and-play, but now if your OS X machine is booted and you connect a USB Ethernet dongle, it will not be recognized, until you reboot the machine with the dongle plugged in. Every time. This feels like Windows to me. I never had to do this with Lion previously.
- There’s a cut-off/echo with the voices in OS X Mavericks. When I have the clock set to announce the time every 15 minutes, instead of “It’s three-fifteen” or “It’s eleven o’clock”, I hear “…ee fifteen” or “…ven o’clock”, the first 1-2 syllables are completely missing, cut off.
There are dozens more that I’ve tripped on (and reported), but they still hamper productive use of the machine.
I also run several apps that depend on Java, including XCode, XMind, The Hit List and others. Most of these just flat-out fail to function. I was so frustrated at the amateurish quality of this major “greatest ever” OS update, that I started investigating myself.
Apple, a plea… how many Java versions, incorrect, non-current Java versions is enough? On this upgraded version of OS X (Lion -> Mavericks), I count 6+ distinct installs!
# OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0-internal-root_2012_07_25_17_59-b00) ./Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Applications/Application Loader.app/Contents/MacOS/itms/java/bin/java # Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_45-b18) ./Library/Internet Plug-Ins/JavaAppletPlugin.plugin/Contents/Home/bin/java # Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_04-b21) ./Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/1.7.0.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java # Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_04-b21) ./Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/1.7.0.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/bin/java # Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_04-b21) ./System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/A/Commands/java # Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.6.0_65-b14-462-11M4609) ./System/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/1.6.0.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java [...]
The only one that is clean and current, is the one I installed:
# "./Library/Internet Plug-Ins/JavaAppletPlugin.plugin/Contents/Home/bin/java" -version java version "1.7.0_45" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_45-b18) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.45-b08, mixed mode)
Of course, you don’t use it anywhere, no apps are referring to it, and instead you refer to the other versions which crash, break or fail to correctly launch any applications that use these Java interpreters.
Please, don’t tout your OS as being the “greatest work ever”, while providing a slow, buggy, de-evolved experience from the previous versions.
Fix it, or allow us to roll back to the previous version of the OS, which did work.
UPDATE: After much testing, I determined that the short-term “solution” was to rm the symlink to ‘java’ in ‘/usr/bin/’ and point it to the version of Java I installed from Oracle, as follows:
$ sudo ls -l /usr/bin/java lrwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 74 Oct 27 15:55 /usr/bin/java -> /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Versions/Current/Commands/java
$ sudo rm /usr/bin/java $ sudo ln -s /Library/Internet\ Plug-Ins/JavaAppletPlugin.plugin/Contents/Home/bin/java /usr/bin/java
After doing this, my Java-based OS X apps started working as expected. This is not a fix, it’s a temporary hack and workaround, but it gets me back up and running on apps that were crashing and failing before.
Apple, please fix this.
SOLVED: Remove annoying duplicate users in your WordPress blog
 This happens quite a bit, and I’m surprised the default WordPress install doesn’t have this fixed, but here’s a fix for cleaning up the duplicate users that will end up in your _users table in WordPress.
This happens quite a bit, and I’m surprised the default WordPress install doesn’t have this fixed, but here’s a fix for cleaning up the duplicate users that will end up in your _users table in WordPress.
In my multi-site installation, that table is called ‘wpmu_users’. If you didn’t change the defaults for your site, it’s probably called ‘wp_users’.
Change this accordingly below for your site and table name.
# Create a temporary table and populate it with the unique users
# from the original wpmu_users table
CREATE TABLE wpmu_users_X AS
SELECT * FROM wpmu_users WHERE 1 GROUP BY user_login;
# Drop the original table that contains the duplicate users
DROP TABLE wpmu_users;
# Rename the temporary table to the original table name. This
# effectively 'moves' the temporary table to the original table
# name
RENAME TABLE wpmu_users_X TO wpmu_users;
# Alter the table attributes to set 'user_login' as a unique key
# so attempts to create a username that already exists will be
# denied
ALTER IGNORE TABLE wpmu_users ADD UNIQUE (user_login);
Here’s what that looked like at the end of the process:
mysql> ALTER IGNORE TABLE wpmu_users ADD UNIQUE (user_login); Query OK, 157348 rows affected (0.55 sec) Records: 157348 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
If you want to identify and kill off inactive users, spammers and such, look into the Inactive User Deleter plugin. I’ve used this with great success on my own blog, and it works great to kill off spam users that manage to sneak past the registration mechanisms, but post nothing.
That’s it, you’re done!
HOWTO: Properly install native VMware Tools in pfSense 2.0.3 (FreeBSD 8.1)
Tags: FreeBSD, Open Source, security, VMware If you’re anything like me, you take security seriously. With all the recent news about the NSA and Prism and over-reach of surveillance, you’ll take this very seriously. I run several layers of nested firewalls, VPNs and other layers of security at my office.
If you’re anything like me, you take security seriously. With all the recent news about the NSA and Prism and over-reach of surveillance, you’ll take this very seriously. I run several layers of nested firewalls, VPNs and other layers of security at my office.
One of the things I run in a virtualized environment (VMware ESXi), is pfSense. pfSense ibs an Open Source firewall distribution based on FreeBSD. It’s very full-featured, has a web-management console, and lots of add-on packages to enhance it’s capabilities.
“pfSense is a free, open source customized distribution of FreeBSD tailored for use as a firewall and router. In addition to being a powerful, flexible firewalling and routing platform, it includes a long list of related features and a package system allowing further expandability without adding bloat and potential security vulnerabilities to the base distribution. pfSense is a popular project with more than 1 million downloads since its inception, and proven in countless installations ranging from small home networks protecting a single computer to large corporations, universities and other organizations protecting thousands of network devices.”
pfSense is currently using FreeBSD 8.1, which has been EOL’d by the BSD team last July. The pfSense team is diligently working on new versions, but they’re not out yet. For now, you can continue to use FreeBSD 8.1.
If you run pfSense inside a VM, you’ll want and need to get the base VMware tools installed within it, but that process isn’t straightforward. You want to make sure you install the VMware Tools dependencies and core modules before installing anything else, so you don’t get into package conflicts and other troubles.
I’ve been writing a lot of posts about VMware lately, because I’m finding myself using it more and more, and I’m teaching myself how to use it in a higher-volume capacity.
Here’s how to install pfSense and immedaitely get the correct version of VMware Tools (from VMware itself, not the Open Source ‘open-vm-toolbox‘ or ‘vmfs-tools’) installed within it.
Let’s get started (click any images below to view them full-size):
- First, create a new VM and attach your pfSense ISO to it, using whatever mechanism your hypervisor of choice provides. Boot it, and install pfSense into your VM. This part is easy and straightforward.
- Once fully installed, shut down (power off) your VM, and detach the CD, so it no longer boots, but keep the CD/DVD device configured for your VM, you’ll use that again in a moment.
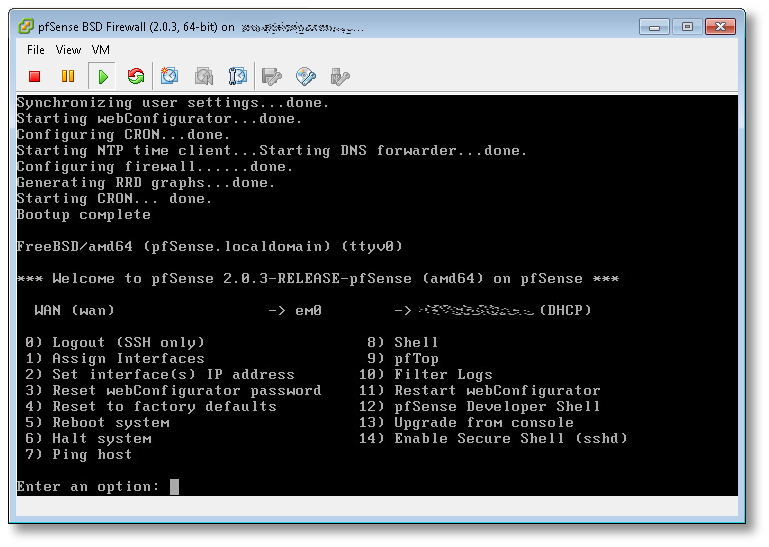
- Boot your pfSense VM back up, configure networking (in my case the NIC was em0), and you’ll get to a screen that looks something like this:
(click image to view full size) - From here, the first thing you want to do, is change your root password! Hit (8) to drop to a shell, and use the standard passwd(1) utility. Once changed, hit ^D (Control-D) to exit and return to the pfSense main menu.
- Next, we’re going to start SSHD, so we can log into the VM remotely, and manage it using a normal Windows, Mac or Linux terminal, vs. interacting with it using the VMware ESXi console (as in this example). Hit (14) to enable the SSH shell.
- In the previous screenshot, directly to the left of the (DHCP) part, was the IP of the pfSense server. SSH over to that now, as the root user, using whatever native terminal you prefer.
$ ssh root@192.168.1.50
- Once SSH’d into pfSense remotely, you’ll need to set the PACKAGESITE environment variable, to make sure all core packging tools refer to the 8.1-release tag from the FreeBSD archive site, and not the 8.1-release-p13 that it will try to use by default from the primary site, which will fail, because FreeBSD 8.1 is EOL as I write this.
-
[2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(1): setenv \ PACKAGESITE \ http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/
Here’s what will happen if you do not set this variable:
[2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(3): pkg_add -rv wget looking up ftp.freebsd.org connecting to ftp.freebsd.org:21 Error: Unable to get ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/wget.tbz: File unavailable (e.g., file not found, no access) pkg_add: unable to fetch 'ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/wget.tbz' by URL pkg_add: 1 package addition(s) failed
Once you set the variable to refer to the archive site, you’ll have success here:
[2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(5): pkg_add -rv wget looking up ftp-archive.freebsd.org connecting to ftp-archive.freebsd.org:80 requesting http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/wget.tbz Fetching http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/wget.tbz...x +CONTENTS x +COMMENT x +DESC x +MTREE_DIRS x man/man1/wget.1.gz x bin/wget ...
- Now we know we can get to the backup/archive site that holds the 8.1 RELEASE packages, let’s get the ones we need to get VMware Tools up and running. We’re going to need two core packages: compat6x-amd64 and perl to be able to run the script and dynamically load the VMware modules at kernel boot.
[2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(6): pkg_add -r compat6x-amd64 perl Fetching http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/compat6x-amd64.tbz... Done. ******************************************************************************* * * * Do not forget to add COMPAT_FREEBSD6 into * * your kernel configuration (enabled by default). * * * * To configure and recompile your kernel see: * * http://www.freebsd.org/doc/en_US.ISO8859-1/books/handbook/kernelconfig.html * * * ******************************************************************************* Fetching http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/ports/amd64/packages-8.1-release/Latest/perl.tbz... Done. Removing stale symlinks from /usr/bin... Skipping /usr/bin/perl Skipping /usr/bin/perl5 Done. Creating various symlinks in /usr/bin... Symlinking /usr/local/bin/perl5.10.1 to /usr/bin/perl Symlinking /usr/local/bin/perl5.10.1 to /usr/bin/perl5 Done. cd: can't cd to /usr/include Cleaning up /etc/make.conf... Done. Spamming /etc/make.conf... Done. Cleaning up /etc/manpath.config... Done. Spamming /etc/manpath.config... Done. - Now we need to mount the CD ISO for VMware Tools for FreeBSD. This is the step I mentioned earlier and why we needed to keep the CD/DVD device configured for this VM. In ESXi, you’ll need to do that from the console, by right-clicking on the VM, go to Guest and then to “Install VMware Tools”, as shown here:
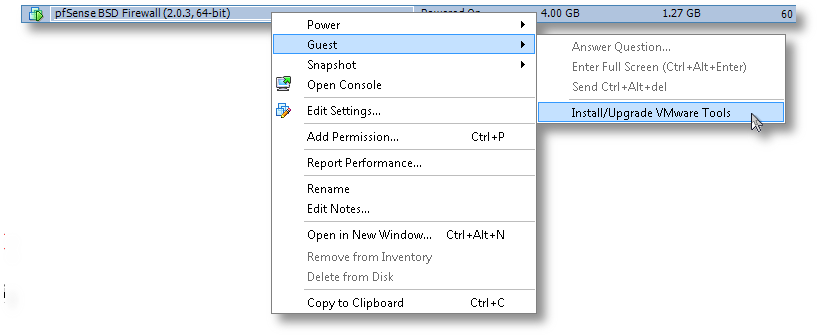
- Now the drive is mapped to the VM, we need to mount it and access the vmware tarball within:
[2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(8): mkdir /tmp/cdrom/ [2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(9): mount_cd9660 /dev/acd0 /tmp/cdrom/ [2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/root(10): cd /tmp/cdrom/ [2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/tmp/cdrom(11): ls -l total 15030 -r--r--r-- 1 root wheel 29 Mar 23 15:02 manifest.txt -r--r--r-- 1 root wheel 15390306 Mar 23 15:02 vmware-freebsd-tools.tar.gz [2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/tmp/cdrom(12): tar zxvf vmware-freebsd-tools.tar.gz -C /tmp/
- Now we can go into /tmp/vmware-tools-distrib and build the required interfaces for FreeBSD. For the most part, you’ll just accept the defaults to most of the questions. Read them carefully if you think you want something custom for your needs.
[2.0.3-RELEASE][root@pfSense.localdomain]/tmp/vmware-tools-distrib(14): ./vmware-install.pl --clobber-kernel-modules=vmci \ --clobber-kernel-modules=vsock \ --clobber-kernel-modules=vmxnet3 \ --clobber-kernel-modules=pvscsi \ --clobber-kernel-modules=vmmemctl Creating a new VMware Tools installer database using the tar4 format. Installing VMware Tools. In which directory do you want to install the binary files? [/usr/local/bin] In which directory do you want to install the startup script? [/usr/local/etc/rc.d] In which directory do you want to install the daemon files? [/usr/local/sbin] In which directory do you want to install the library files? [/usr/local/lib/vmware-tools] The path "/usr/local/lib/vmware-tools" does not exist currently. This program is going to create it, including needed parent directories. Is this what you want? [yes] In which directory do you want to install the documentation files? [/usr/local/share/doc/vmware-tools] The path "/usr/local/share/doc/vmware-tools" does not exist currently. This program is going to create it, including needed parent directories. Is this what you want? [yes] The installation of VMware Tools 9.0.5 build-1065307 for FreeBSD completed successfully. You can decide to remove this software from your system at any time by invoking the following command: "/usr/local/bin/vmware-uninstall-tools.pl". Before running VMware Tools for the first time, you need to configure it by invoking the following command: "/usr/local/bin/vmware-config-tools.pl". Do you want this program to invoke the command for you now? [yes] Initializing... Making sure services for VMware Tools are stopped. Stopping VMware Tools services in the virtual machine: Guest operating system daemon: done The vmblock enables dragging or copying files between host and guest in a Fusion or Workstation virtual environment. Do you wish to enable this feature? [no] No X install found. Starting VMware Tools services in the virtual machine: Switching to guest configuration: done Guest memory manager: done Guest operating system daemon: done The configuration of VMware Tools 9.0.5 build-1065307 for FreeBSD for this running kernel completed successfully. You must restart your X session before any mouse or graphics changes take effect. You can now run VMware Tools by invoking "/usr/local/bin/vmware-toolbox-cmd" from the command line. Please remember to configure your network by adding: ifconfig_vxn0="dhcp" to the /etc/rc.conf file and start the network with: /etc/netstart to use the vmxnet interface using DHCP. Enjoy, --the VMware team
That’s it. You’ve now got a working VMware Tools install using the native, VMware-provided kit, inside your VM. If you’re running ESXi, you’ll now notice that it correctly reports its version, status and IP back to the console, which was missing before we started.

Good luck!
Using fdupes to Solve the Data Duplication Problem: I’ve got some dupes!
Well, 11.6 hours later after scanning the NAS with fdupes, I noticed that I’ve got some dupes across my system backups.
# time ./fdupes -R -Sm "/nas/Backups/System Backups/" 2153352 duplicate files (in 717685 sets), occupying 102224.5 megabytes real 698m15.606s user 38m20.758s sys 92m17.217s
That’s 2.1 million duplicate files occupying about 100GB of storage capacity in my backups folder on the NAS. DOH!
Now the real work begins, making sense of what needs to stay and what needs to get tossed in here.
UPDATE: I may give up on fsdupes altogether, and jump to rmlint instead. rmlint is significantly faster, and has more features and functions. Here’s a sample of the output:
# rmlint -t12 -v6 -KY -o "/nas/Backups/System Backups/" Now scanning "/nas/Backups/System Backups/".. done. Now in total 3716761 useable file(s) in cache. Now mergesorting list based on filesize... done. Now finding easy lint... Now attempting to find duplicates. This may take a while... Now removing files with unique sizes from list...109783 item(s) less in list. Now removing 3917500 empty files / bad links / junk names from list... Now sorting groups based on their location on the drive... done. Now doing fingerprints and full checksums.. Now calculation finished.. now writing end of log... => In total 3716761 files, whereof 1664491 are duplicate(s) => In total 77.66 GB [83382805000 Bytes] can be removed without dataloss.
HOWTO: How to Fix a Forgotten Windows Administrator or User Password with Sticky Keys
I pulled some of my very old Windows VMs out of my backup NAS recently with the intent to pull them into ESXi 5.0.1, and manage them there.
But they hadn’t been booted or updated in 4+ years. I thought I remembered the password for the users of these VMs, but none of my obvious choices worked.
I tried getting into it by booting an ISO loaded with chntpw to blank the Administrator password, but that didn’t work. I tried enabling the Guest account and setting a password there (also with chntpw), but that failed as well.
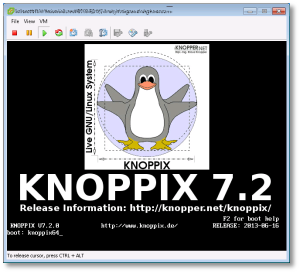
So the next option was to boot up a KNOPPIX DVD in my VM, and follow these steps to reset the password using the “Sticky Keys” trick:
Click image to open full size
- Boot from the KNOPPIX DVD (or Windows PE, Windows RE) in your Windows machine or VM. When you get to the boot prompt, type the following to get a 64-bit environment:
- Let the OS load (graphical or otherwise) and open a shell session (Linux “command prompt”). You’re going to manually mount the Windows drive here, and copy some files around.
- sudo to root
$ sudo su -
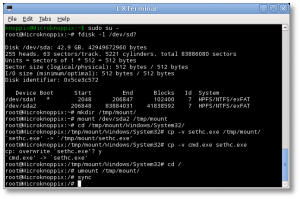
- At the shell, find your Windows drive. It will typically be something like /dev/sda1, as seen from KNOPPIX. The following fdisk(1) command will help you find it:
# fdisk -l /dev/sd?
- Now you’ll need to mount that drive to access it:
# mkdir /tmp/mount # mount /dev/sda1 /tmp/mount # cd /tmp/mount
- Change to the System32 directory under the Windows directory in your temporary mountpoint. Note that depending on your OS version, this may have a different case sensitivity. It may be “Windows”, “WINDOWS”, or “WinNT”.
# cd /tmp/mount/WINDOWS/System32
- Now we can preserve and copy files that will help us get into the machine. In this next step, we’re going to back up a copy of “sethc.exe” to the root of the C:\ drive. This is a backup copy we’ll use to restore later, once we’re able to log into the machine.
# cp -v sethc.exe /tmp/mount/ # cp -v cmd.exe sethc.exe
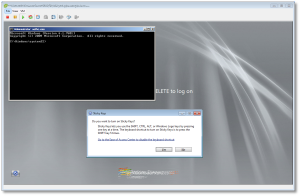
- Now you can unmount the drive, shut down your machine, disconnect the KNOPPIX DVD and boot back up to the drive natively, back to the point where you forgot the Administrator or user’s password.
# cd / # umount /tmp/mount/ # sync # poweroff
- Once your machine has fully booted, after you see the logon screen, press the SHIFT key five times. Do not hit Ctrl-Alt-Del here, just hit [shift] 5 times in a row. If you’ve done it right, you should see a Windows command prompt where you can enter the following command to reset the Windows password.
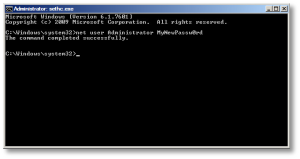
C:\Windows\System32\net user Administrator MyNewPassw0rd
Or if you need to just reset a non-Administrator account password, replace ‘Administrator’ in the above command with the appropriate username. If you don’t know your user name, just type the following to get list the available user names:
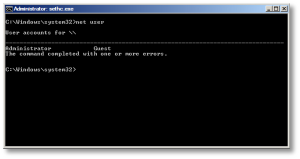
C:\Windows\System32\net user
- You should now be able to log on with the new password you just created.
- Don’t forget to restore C:\seth.exe to C:\Windows\System32\seth.exe, or anyone with access to your machine will be able to use the same trick to reset your password and breach your account! To do that, follow the same steps above (boot to KNOPPIX, mount drive, copy files) to replace the backed-up copy of the original file. You won’t be able to do this while the machine is booted, as those files are locked and will not be replaceable.
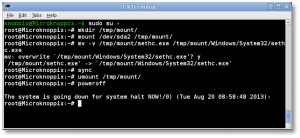
That’s it! Now you’ve got your password recovered, and you can log in without issues.
Note: If you want to prevent someone from using this same trick, or using Kon-Boot against your server, you need to install and configure full-disk encryption with a tool like TrueCrypt. Do not use Microsoft’s “Bitlocker” product, as it is easily cracked.
DomainSite: This is Not the Way to Manage Passwords
Tags: DNS, Domainsite, securityAs per my end-of-month processing, I update and rotate/change the passwords and login credentials for the hundreds of websites and logins I own and use on a regular basis.
I reached my domain registrar, DomainSite, and successfully changed my password to something nice and secure, and their system happily accepted it.
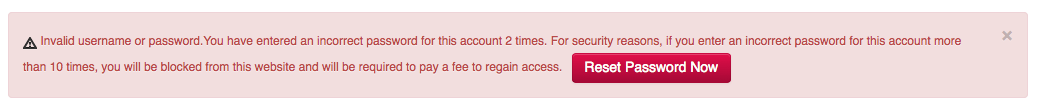
I logged out, and attempted to log in with that new password to verify that it was a successful change, and was denied. I tried again, denied again, and then I received this message from their system:
“For security reasons, if you enter an incorrect password for this account more than 10 times, you will be blocked from this website and will be required to pay a fee to regain access.”
Not only is this an unhelpful message, but it also puts the burden on the owner of the account to pay up if someone else decides to try to lock out their account.
In other words, I can attempt to log into DomainSite as another user more than 10 times, and now that user will have to pay Domainsite to restore their password.
Seriously, who thought this up? In my multi-decade experience of using the Web, I’ve never heard of a single case of someone attempting to charge the owner of a valid login credential, for an account that was locked out and had to be reset or restored.
DomainSite, tsk, tsk! You should know better!
If you’re going to permit someone to change their password legitimately, verify the password or at least describe the password policy so we can decide how complex we can make our passwords, before we lock ourselves out, because your system fails to clarify this on both sides.